PRY
What is PRY
PRY is a bio-economic livestock herd/population model developed by Dr. habil. Richard Baptist (formerly of the University of Nairobi and the University of Hohenheim) in 1988. PRY is a species independent, livestock-driven, herd model, which combines deterministic and stochastic procedures and allows for assessing herd/population productivity, simulating herd/population development, comparing productivity between livestock systems and management strategies within livestock systems.
PRY derives a productivity index (PI) "total output value/dry matter intake (TOV/DMI)" as a measure of overall productivity of an animal production system. Dry matter intake is chosen as denominator in this index because feed is considered the most limiting production asset as it generally accounts for the major part of production costs and is the main input factor in extensive animal husbandry systems.
PRY in its original DOS based version consists of six single components or modules (DIC, PIC, SAM, FOC, BOI, APE). Demographic input parameters are entered and stored in DIC. Produce-related input parameters are entered and stored in PIC. Deterministic modelling components SAM, FOC, and BOI derive population structure, numeric offtake, life expectancies and potential rate of increase of population for an infinitely large, closed equilibrium population (a population at steady state) from the DIC parameters. Total offtake value per dry matter intake for different disposal strategies is derived adding information from the PIC parameters, thus the model permits to find an optimal culling strategy (FOC). With a specific culling regime specified, a detailed breakdowns of offtake and intake (BOI) can be derived. The stochastic animal population emulator APE permits the simulation of herd/population development over time.
PRY was further developed by Dr. Richard Baptist into an MS Excel add-in named HerdLife. HerdLife combined the different modules above and eased handling of the model, particularly parameter input as well as display and storage routines.
In a current effort encouraged by the model author, PRY / HerdLife will be linked to external data sources – i.e. spreadsheet or database applications often used in research projects as well as livestock management programmes such as CowSense (TM by Midwest Microsystems). Thus, input parameters can be directly read/retrieved from data either routinely collected in commercial livestock operations or data generated by research projects. The initiative is carried forth by a consortium between Science Data Services (Dr. Simon Riedel), the German Institute for Tropical and Subtropical Agriculture [www.ditsl.org DITSL] (Dr. Christian Hülsebusch and Prof. Dr. Brigitte Kaufmann) and the University of Kassel (Dr. Uwe Richter, Prof. Dr. Eva Schlecht). The consortium appreciates the generous permission of the author, Dr. habil. Richard Baptist, to further develop his valuable tool with the aim to provide a flexible decision support tool for the management of livestock systems.
In a first step, the model was transcribed into a standalone application running under Windows XP/7 named PRY 3.0 beta – which can be downloaded here for test purposes
In a next step, a MySQL database will be coupled to PRY 3.0 beta that permits translation of CowSense (TM by Midwest Microsystems) export data into demographic input parameters for PRY.
DIC - Demographic Program Input Constants
Purpose of DIC PRY provides an interactive routine for entering demographic parameters or inherent fitness traits. These are: survival rates, selective culling rates, age at first parturition, parturition interval and litter size. This routine is referred to as DIC (Demographic Program Input Constants). At every step of parameter entry, checks are carried out, error messages displayed and only consistent values accepted to avoid crashing of the simulation and derivation routines. Specification of age groups, rates and histograms is flexible. After entry, the parameters are formatted and saved to a work file from which they are later retrieved by the simulation and derivation routines.
Survival Rates
A survival rate is the fraction of animals still present at the end of a time interval if no living animal were disposed of. Such a rate represents an inherent potential and can be specified even for age classes which, in practice, are not at all represented because animals are culled before that age. Survival rates observed under a specific culling pattern may well differ from the survival rates to be specified as inherent demographic parameters. Survival rates can be specified for arbitrary age classes as either an annual rate or as a fraction surviving to the end of the specified interval. Such an interval or age class is defined in terms of a starting week or month of age and an ending week or month. The period covered can be more or less 8than a year.
Animals surviving to the ’biological’ maximum age specified, are assumed to be lost, rather than culled at the last time-step. However, animals
surviving to a cull-for-age threshold lower than the ’biological’age limit,are assumed to be culled.
If only one survival rate per sex is specified, the age group then includes all ages from the first month or week of age up to the highest possible age.
A maximum of 14 age groups can be defined. Male and female survival rates may be the same. However, age group boundaries and corresponding
rates can also be defined for each sex separately.
Losses and culls in breeding females are not always clearly distinguishable. Emergency slaughter is an anticipated mortality or a cull, depending on the value of deadweight. Youngstock is never disposed of on voluntary grounds unless it has reached ’marketing’ age. Therefore, forced culls in
youngstock are to be aggregated with losses. The value of deadweight can be adjusted correspondingly, to reflect an expected average of real losses of low salvage value and forced cullings of high salvage value.
APE - Animal Population Emulator
SAM - Stationary-State Animal Demographic Model
PIC - Produce-Related Program Input Constants
FOC - Find optimal Culling Ages
Bio Breakdown of Offtakes and Intake
The Algorithms
Before you Start
Hardware Requirements
| System Architecture | This system runs on 32 and 64bit Systems |
| Operation System | Microsoft Windows |
| Win Version | Win 7, Win 8, Win 10 |
| HDD Space required | 300MB |
| RAM | 2 GB (4 Recommended) |
| Misc | Requires the Installation of some Database-Modules from Microsoft |
Download
Unless you are a developer or require Modules from the original DOS Software, you most proably want to use the 3.x Version of the Software, provided as an installable Windows App. Download of other Versions below
PRY 3.x
Latest Version
| Version | File | ReleaseNotes |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0.13 | PRY 3.0.12 Windows Installer | abcdef.txt |
Access previous Versions of PRY
Installation Manual
| Requirements | |
| What | Description |
|---|---|
| PRY Installer | Get the PRY Zip File (here) |
| Unzip Software | WinRar, WinZip or 7zip - you most probably have such Software on your computer |
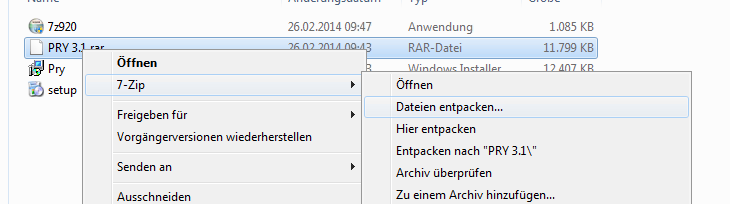
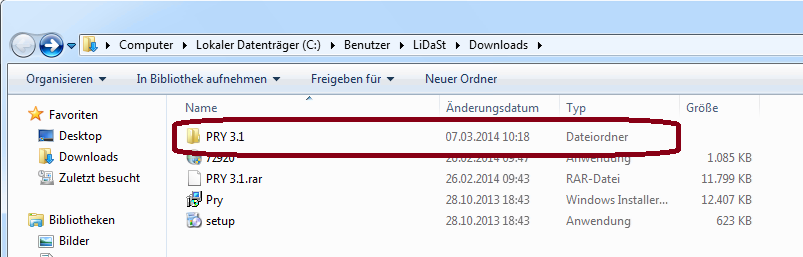
1.) Extract the Zip File into any Folder
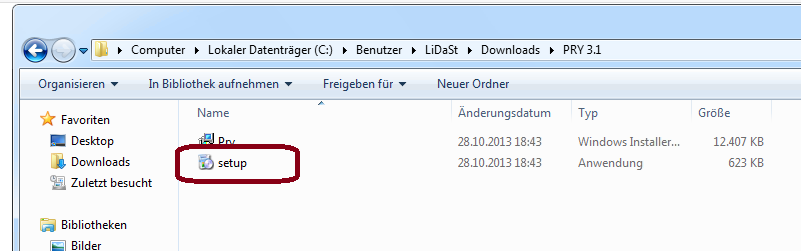
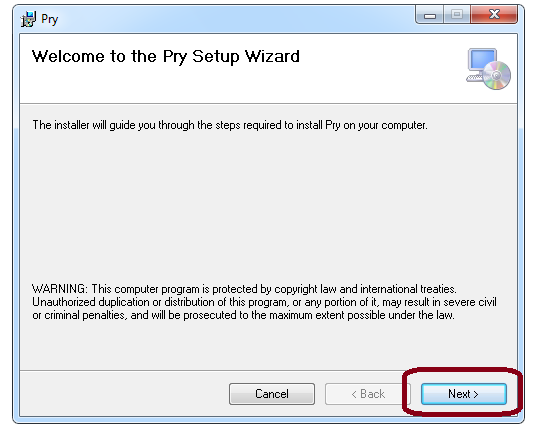
2.) Open the Folder and click on "Setup.exe"
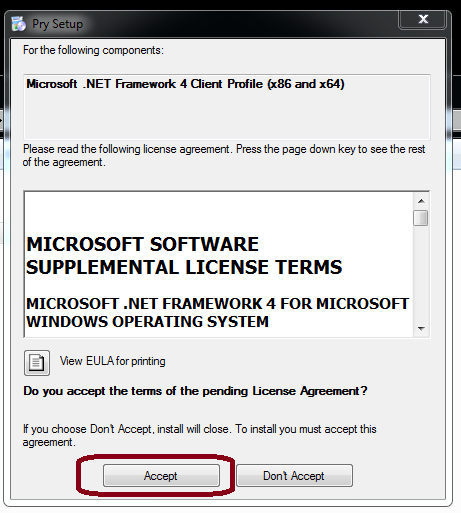
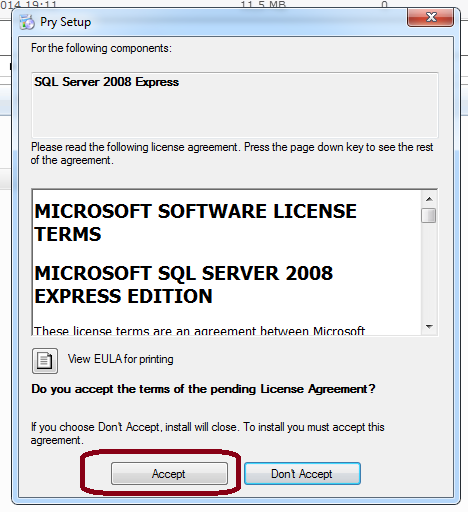
3.) Two modules will be directly downloaded from Microsoft - if you don't already have them installed on your computer, you need to agree to the Terms and Conditions and follow the installation instructions of those modules
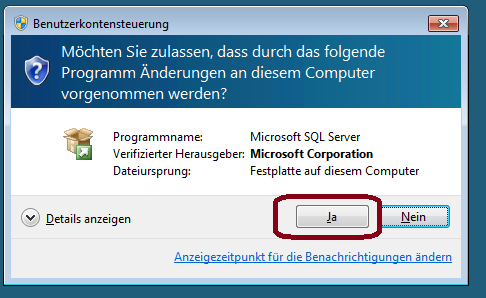
4.Allow Microsoft to install Modules on your Computer
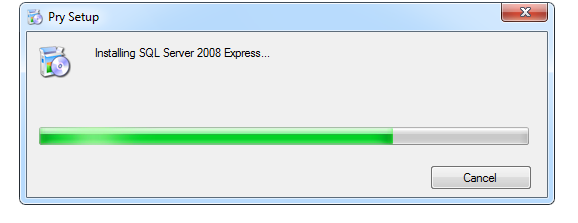
5. The installation is in process
PRY' is now successfully installed on your Computer. You will find a Link to the Software on your Desktop (Icon is black, so you might not see it directly when your Background is black) and in the Start-Menue.
If you encounter any problem with installing PRY on your computer, you may ask for support
User Manual
For other Versions see User Guide here
- Version 2.x
- PRY realized as Modules in an Excel sheet
- Version 1.x
- The original PRY, a DOS console Program
Model Input Parameters
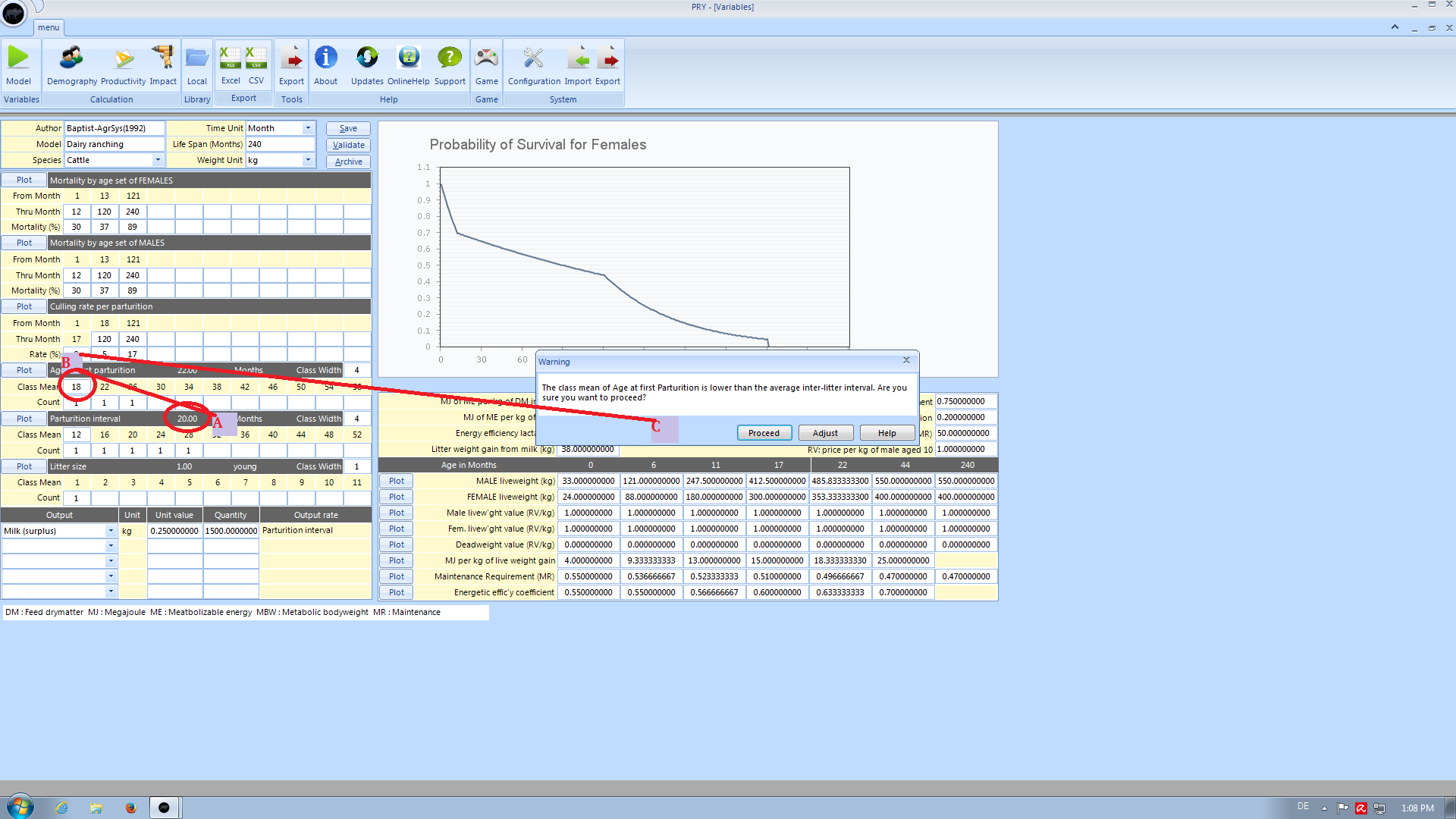
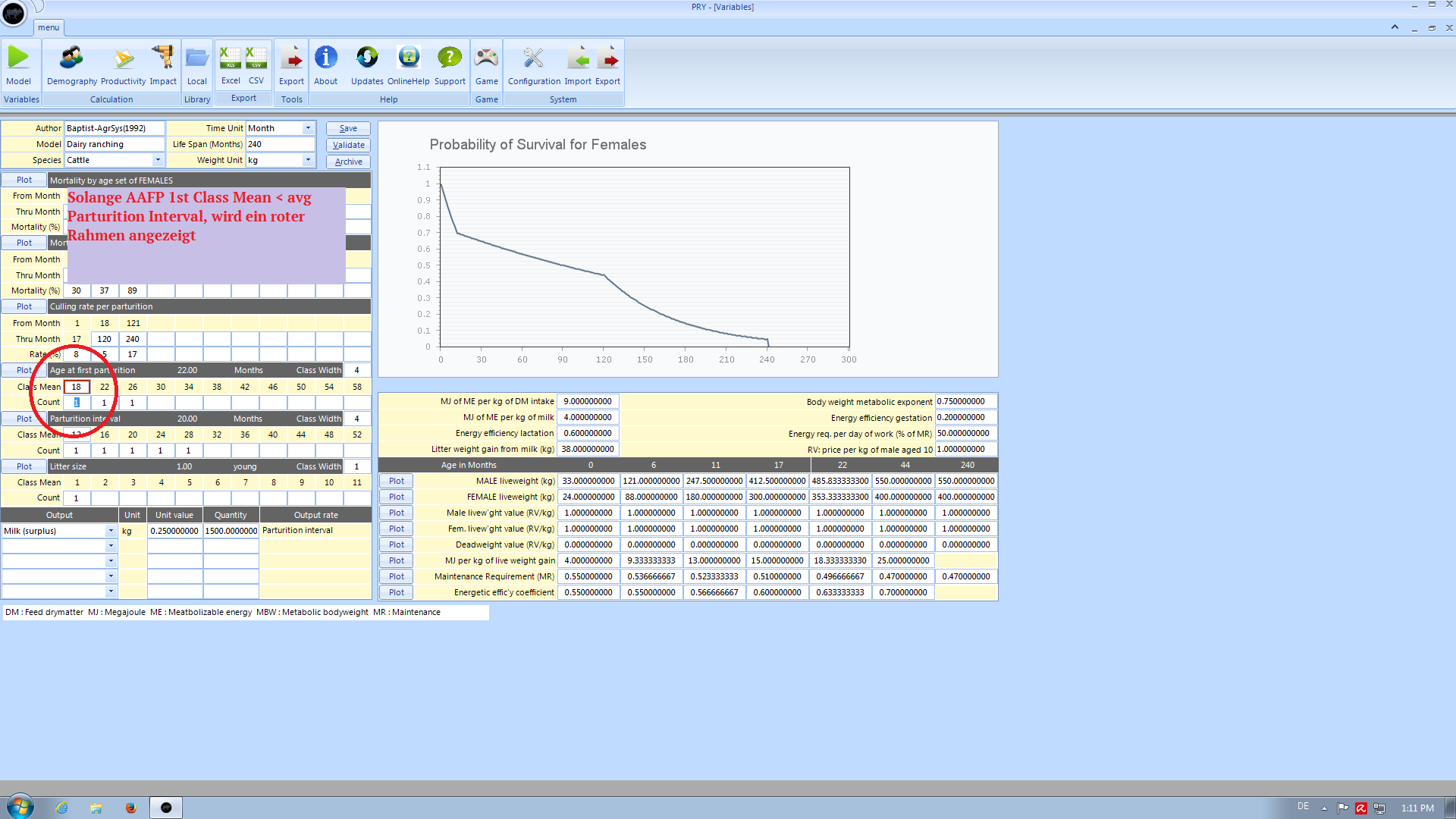
Age at first Parturition
When a class mean in the first class of age at first parturition is entered which is below the average inter-litter interval, a warning shows up to recheck your values. You have three options:
- Proceed and leave your input as it is
- Correct your value
- Click the Help Button to learn why this value might be critical for your model
Technical Documentation
Literature
Many studies have been conducted by using the PRY Software. We are trying to collect all, so if you know of any further study, let us know, we will list them here. If you have any questions about those publications, you may contact DITSL , visit the [contact] page for further details.
Herd Analysis with PRY
| Author | Year | Journal | Title | Link/File | Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baptist,R. Sommerlatte | 1992 | Small Ruminant Research | Evaluation of cropping strategies in game ranching using a livestock productivity model | http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0921-4488(91)90124-9 | Game |
| Fink H. and Baptist R. | 1992 | Better feeding for improved production - FAO Series | Herd dynamics modelling applied to a venison ranch in Kenya | http://www.fao.org/docrep/u8750t/u8750T04.htm | Game |
| Anonymous | 1995 | Wildlife and Nature | Herd Dynamics modelling applied to a Venison ranch in Kenya | Game | |
| Fink | 1990 | unpublished (Diploma Thesis) | Schätzung demographischer Parameter in der Wildnutzung aus ermitteltem Propulationswachstum und -struktur, Entnahmerate und Zusammensetzung der Entnahme auf einer kenyanischen Wildranch | DOI | Game |
| Kaufmann, B. | 199x | contact | Cattle/Camel | ||
| Huelsebusch, C. | 199x | contact | Cattle/Camel | ||
| Dos Santos / Neuzling, A. | 200x | contact | Cattle | ||
| Dickhoefer et al. | 2012 | Agricultural Systems 110,C, 131-141 | Modeling herd development and revenues from Jabal Akhdar goats under current and intensified management | http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0308521X12000583 | Goat |
| Riedel et al. | 2014 | Livestock Science, 160, 151-162 | The productivity of traditional smallholder pig production and possible improvement strategies in Xishuangbanna, South Western China | http://www.livestockscience.com/article/S1871-1413%2813%2900502-7/abstract | Pigs |
| Hofsommer | 2014 | contact | Cattle | ||
| Aufderheide, M. | 2014 | contact | Cattle | ||
| Wario, H.T. | 2015 | Social Ecological Research Series | An integrated assessment of resource use strategies in the Borana pastoral system of southern Ethiopia | http://d-nb.info/1075658810/34 | Cattle |
Methodology
| Author | Year | Journal | Title | Link/File |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baptist, R. | 1987 | Agricultural Systems | Computer Simulation of Monitoring Herd Productivity under extensive Conditions: Sampling Error of Herd Size and Offtake Rate | http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0308-521X(87)90003-5 |
| Baptist, R. | 1988 | Agricultural Systems | Herd Flock Productivity Assessment using the Standard Offtake and the Demogram | http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0308-521X(88)90022-4 |
| Baptist, R. | 1991 | unpublished | PRY Manual | |
| Baptist, R. | 1992 | Habilitation | Population Dynamics and Productivity at the stationary State of Culling Regimes in Livestock Herds and Flocks | |
| Pittroff and Cartwright | 2002 | Arch. Latinoam. Prod. Anim. | Modeling livestock systems. I. A descriptive formalism | http://www.alpa.org.ve/PDF/Arch%2010-3/Archivos10(3)193.pdf |
| Rushton, J. | 2009 | CABI Publishing | The Economics of Animal Health and Production , p. 96 | ISBN 1845931947 |